 Thermal Oxidizers
Thermal Oxidizers
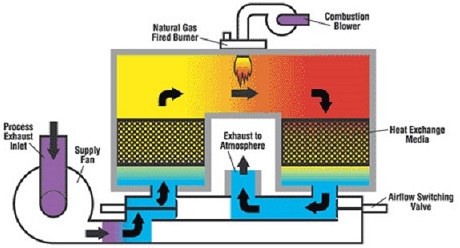
Thermal oxidizers, or thermal incinerators, are combustion devices that control VOC, CO, and volatile HAP emissions by combusting them to carbon dioxide and water. Design factors include temperature, residence time, and turbulence or mixing of the combustion air with the waste gas.
To reduce fuel usage required for oxidation, thermal oxidizers frequently have some form of heat recovery. The percentage of heat recovery in the design of thermal oxidizers generally increases with decreasing inlet VOC/HAP concentration. Heat recovery may either be recuperative or regenerative. In recuperative heat recovery, heat is recovered by passing the hot exhaust gases through a non-contact air-to-air heat exchanger, to heat the incoming air to the oxidizer. In regenerative heat recovery, hot exhaust gases and cool inlet gases are alternatively passed through a fixed bed, typically employing ceramics.
Pacific Environmental Engineering Corp.
email pe@4voc.com